(O1) First Derivative Test#
By the end of the lesson you will be able to:
find all critical numbers of a function.
classify all critical numbers using the first derivative test.
Critical Numbers#
First Derivative Test#
Second Derivative Test#
Example 1#
Example 2#
Example 3#
One Critical Number#
Example 4#
Finding Local Extrema#
Fermat’s Theorem
If \(f\) has a local maximum or minimum at \(x=c\), then either \(f'(c)=0\) or \(f'(c) \; DNE\).
Critical Number
The number \(x=c\) is a critical number of \(f\) provided either:
and \(c\) is in the domain of \(f\).
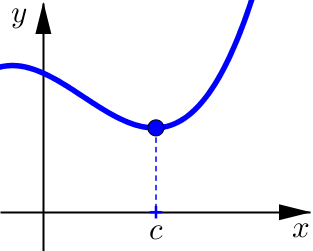
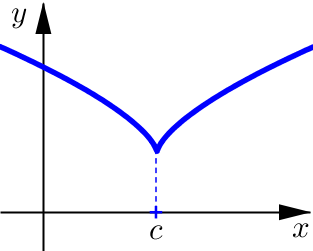
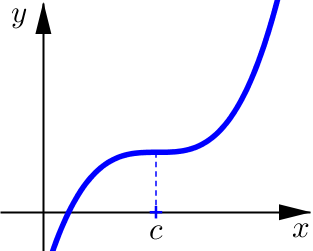
Classifying Critical Numbers#
First Derivative Test for Local Extrema
Let \(x=c\) be a critical number of continuous function \(f\).
If \(f'\) changes from \(+\) to \(-\) at \(c\), then \(f(c)\) is a local maximum.
If \(f'\) changes from \(-\) to \(+\) at \(c\), then \(f(c)\) is a local minimum.
If \(f'\) does not change signs at \(c\), then \(f(c)\) is not a local extremum.
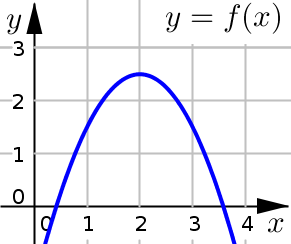
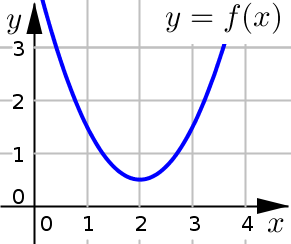
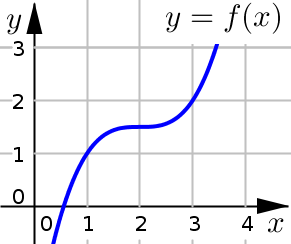
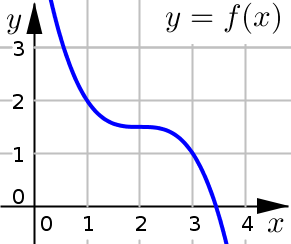
Example 1#
Function \(f\) is a function with domain \((-\infty, -3)\cup(-3,\infty)\) with first derivative given below. Find and classify all critical numbers of \(f\).
Example 2#
Find the local maximum and minimum values of:
Example 3#
Find the local maximum and minimum values of:
Example 4#
Find the local maximum and minimum values of:
Example 5#
Find the local maximum and minimum values of:
