(DG1) Graphically Finding Intervals of Increase / Decrease#
By the end of the lesson you will be able to:
locate the intervals of increase and the intervals of decrease given the graph of a function.
locate the local maximums and local minimums given the graph of a function.
Lecture Videos#
Increasing / Decreasing#
Extreme Values#
Concavity#
Example 2#
First Derivative Rule#
Second Derivative Rule#
Examples 5 and 6#
Example 7#
Increasing / Decreasing#
Increase / Decrease
Increasing on an Interval: the graph continuously rises as \(x\) goes from left to right through the interval.
Decreasing on an Interval: the graph continuously falls as \(x\) goes from left to right through the interval.
Example 1#
Determine if the following graphs are increasing, decreasing, or neither at \(x=c\).
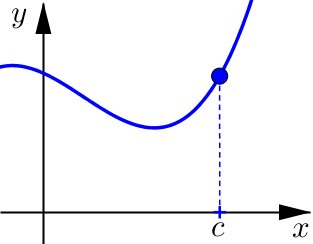
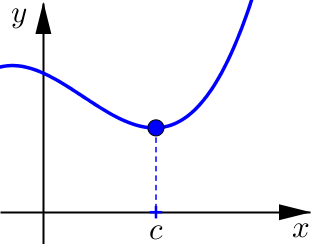
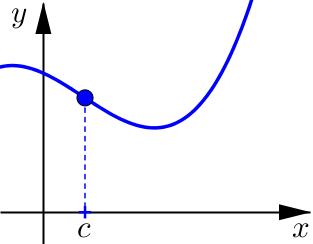
Relative Maximum and Minimum#
Relative Maximum / Minimum
A local maximum value of \(f\) is a number \(f(c)\) such that \(f(c)\geq f(x)\) for \(x\) near \(c\).
A local minimum value of \(f\) is a number \(f(c)\) such that \(f(c)\leq f(x)\) for \(x\) near \(c\).
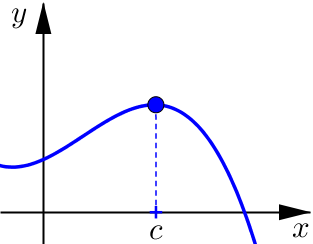

Example 2#
Use the graph of \(y=f(x)\) given below to find:
all intervals of increase and all intervals of decrease
the \(x\)-values of all local maximums and local minimums
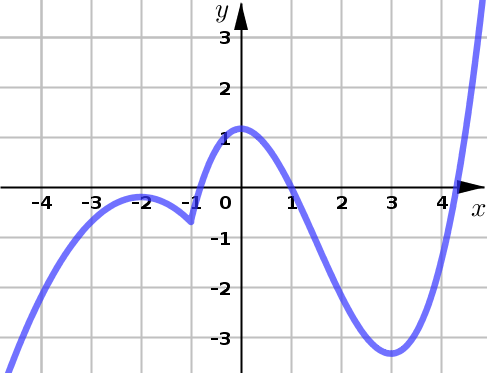
Example 3#
Use the graph of \(y=f(x)\) given below to find:
all intervals of increase and all intervals of decrease
the \(x\)-values of all local maximums and local minimums
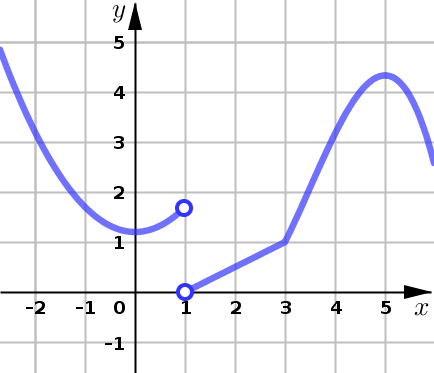
Critical Number
The number \(x=c\) is a critical number of \(f\) provided either:
and \(c\) is in the domain of \(f\).
